![]()
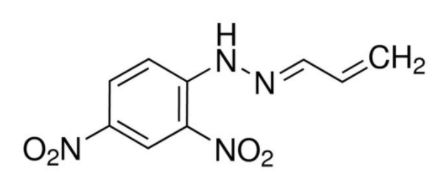
Acrolein (DNPH Derivatives) Certified Reference Standard
Supplied with a Certificate of Analysis
Testing for Acrolein is increasing
Links to Cancer and Alzheimers explored as concerns of Acrolein found in Tobacco Smoke (including vapes) and vehicle exhaust fumes emerge.
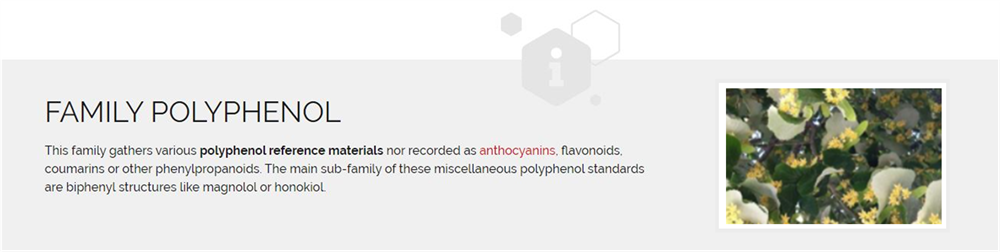
WHAT IS ACROLEIN?
Acrolein is either a yellow colored or clear liquid that is known to both evaporate and burn quite easily. Another known trait of Acrolein is that it has a strong, foul smell. When it is exposed to other substances, it can react even more quickly. Acrolein is also typically used as an herbicide to kill weeds. However, it has purposes in a variety of industries, from papermaking, producing acrylic acid, and controlling bacteria and microorganism growth.
Is Acrolein Toxic?
Yes. Acrolein is known to potentially cause cancer if in a high enough concentration. Although Acrolein is found in small amounts in certain food (such as coffee or some cooking oils) and tobacco smoke, it generally is not ingested in high enough quantities for any serious health effects to occur. However, certain industry workers, like in coal plants and firefighting, can be exposed to higher levels of Acrolein that may result in serious health problems. High exposure to Acrolein can result in Acrolein poisoning, and you should seek medical attention if you believe you have been exposed to high levels of Acrolein.
What are the Health Risks of Acrolein?
When breathed in, lower levels of Acrolein may irritate the nose, nasal cavity, voice box, and esophagus. Additionally, Acrolein can cause fluid to build up in the lungs when inhaled. If someone with Acrolein poisoning does not seek medical attention, severe damage to the lungs and respiratory system could occur, resulting in death. Acrolein may also cause severe damage to the digestive tract, as well as the mouth, lips and throat if it is ingested in any way. This could potentially cause flu-like symptoms, such as vomiting and diarrhea. Acrolein can also damage the eyes of someone if it manages to get into their eyes. Furthermore, high levels of Acrolein could result in potential damage to the central nervous system.
Is Acrolein Found in Vapes?
According to the American Lung Association, Acrolein is found in not just cigarettes, but also in vapes. In the concentration that is found in vapes, this could cause COPD, difficulty breathing, asthma, and even lung cancer.
Is Acrolein Found in Food?
Acrolein is found in food. As mentioned earlier, Acrolein is found in a variety of different foods. Acrolein is typically found in both plant and animal fat, and when those are cooked they do release small amounts of Acrolein. This means that when you eat fried and fatty foods, you may be exposed to higher levels of the substance. Cooking oils and roasted coffee are also known to carry small levels of Acrolein.
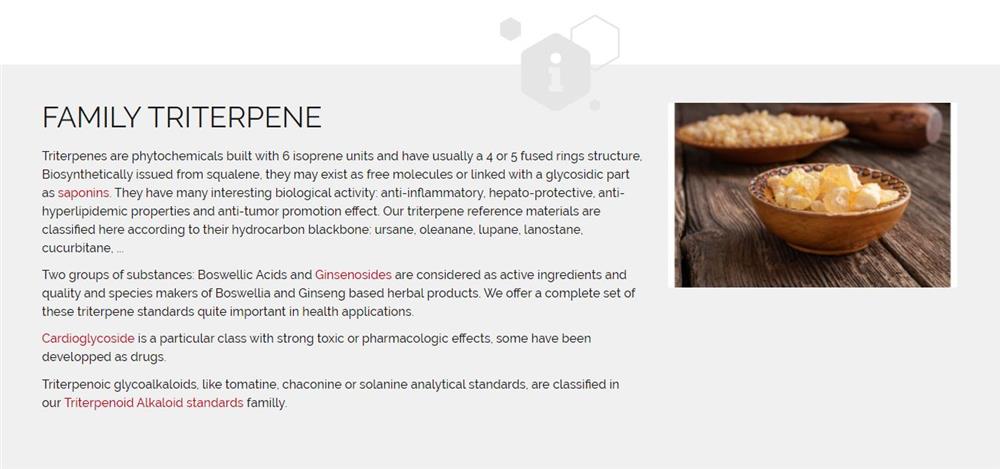
How is Acrolein Produced?
Acrolein is produced industrially by oxidizing propene in a process that uses air as the oxygen source and combining them with metal oxides and certain catalysts. However, it can also be produced using condensation of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. Acrolein is typically used as a contact herbicide, typically in water-based environments. In the EPA’s Method 603 to test for Acrolein in wastewater, an inert gas is bubbled through a 5mL water sample that is in a heated purging chamber. This transfers Acrolein into a vapor phase. This vapor is then sent through a trap that separates the compounds, which is then heated and backflushed with inert gas to transfer the compound into a gas chromatographic column. The EPA’s Method 624.1 is very similar to Method 603, but has an added step where the column has temperature programming to separate purgeable materials, which is then determined with a mass spectrometer.
How is Acrolein used to Test for the Presence of Glycerin or Fats?
This method is called the “Acrolein test”. In this method, a sample of fat or glycerin is heated with potassium bisulfate- if Acrolein is released during this test then the results are positive. When a dehydrating agent is heated along with a fat, the molecules’ glycerol portion will dehydrate and form Acrolein, which smells similar to burnt cooking oil.
What is the Acrolein-Azide “Click Reaction” and Endogenous Acrolein?
Scientists have noticed that aryl azides can and will quickly select and react with Acrolein, called a “click reaction”. These then form 4-formyl-1,2 3-triazolines, and 4-formyl-1,2,3-triazoles, much of which are unexplored reactivities of these aryl azides. For Endogenous Acrolein, the main sources are from myeloperoxidase-mediated degradation of threonine and amine oxidase-mediated degradation of spermine and spermidine.
How can Chem Service Acrolein Analytical Standards be used?
Chem Service's analytical standards help analysts clients identify the presence of acrolein in their testing samples. With our products, testing services will not only be able to identify the presence of acrolein, but also will be able to determine how pure the chemical is. Using the result of our testing samples, you’ll be able to provide their clients with informative testing results that are also easy to understand.
References:
- Dietrich Arntz; Achim Fischer; Mathias Höpp; et al. (2012). “Acrolein and Methacrolein”. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_149.pub2
- Abraham, Klaus; Andres, Susanne; Palavinskas, Richard; Berg, Katharina; Appel, Klaus E.; Lampen, Alfonso (2011). “Toxicology and risk assessment of acrolein in food”. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 55: 1277–1290. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100481
- M J Dykstra, L E Reuss (2003). Biological Electron Microscopy: Theory, Techniques, and Troubleshooting. Springer. ISBN 0-306-47749-1.
- Unexplored Chemical Reactions of Endogenous Acrolein: Detection, Toxicity, and Biological Roles, Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(3):301-306. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.16-00231-3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28250324/
- Toxicological Profile for Acrolein, https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp124-c2.pdf
- Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet – Acrolein https://www.nj.gov/health/eoh/rtkweb/documents/fs/0021.pdf
- American Lung Association, “Impact of e-cigarettes on Lungs”, https://www.lung.org/getmedia/e5325d10-11fa-4b17-aaed-312e135b4100/impact-of-ecigarettes-on-lung.pdf.pdf
- Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 Jun 9. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 Jan; 52(1): 7–25.
doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700412, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2423340/
Article originally published JULY 21, 2021
CONTACT US
Tel: +44 (0) 151 649 4000
Email: marketing@greyhoundchrom.com
FOLLOW US
YOU MAY ALSO BE INTERESTED IN OUR NEWSLETTER




































-L-Alllin Structure V4.JPG)